SPECIFIC LACERATIONS: Lip
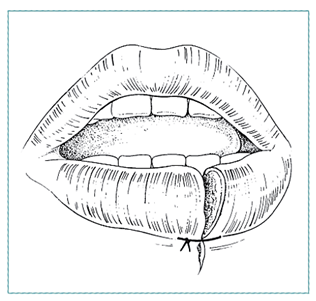
 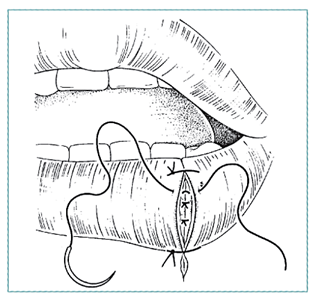 |
| Initial stitch at border Repair in layers: mucosa, muscle Suture skin last |
SPECIFIC LACERATION: Tongue
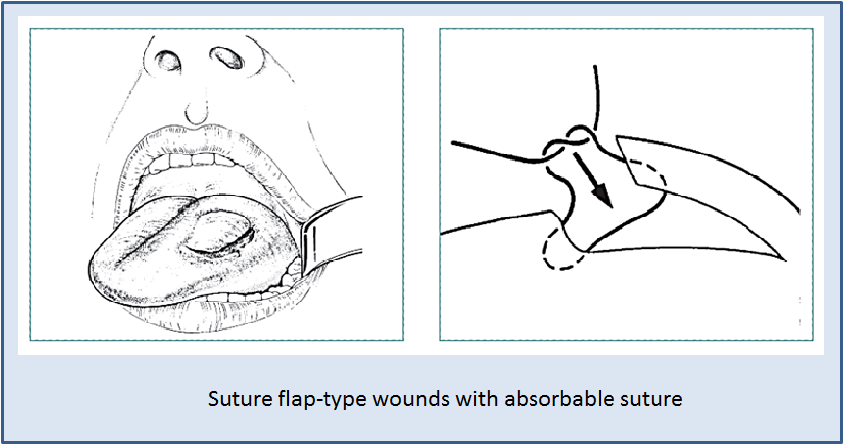
SPECIFIC LACERATIONS: Ear
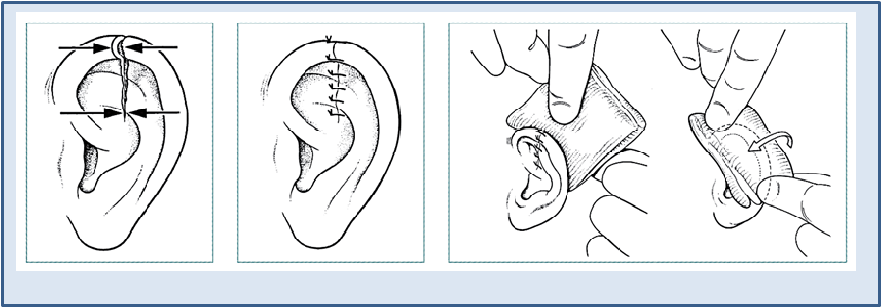
- Use folds of ear as landmarks
- Use absorbable suture for cartilage
- Support pinna on both sides with gauze
SPECIFIC LACERATIONS: Eyelid
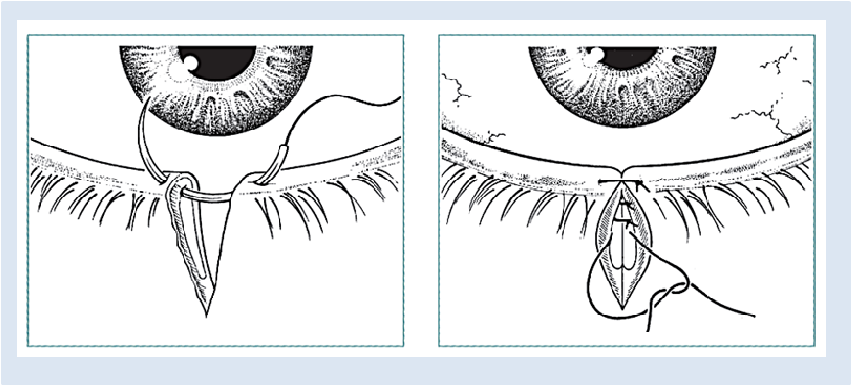
Initial suture for precise alignment Closure in layers: absorbable suture
HAND: Treatment of Lacerations
- Check circulation, sensation, motor function
- Gently examine wound using aseptic technique to determine if clean or contaminated: contaminated wound contains foreign material, crushed or dead tissue
- Debride, lavage all wounds in operating theatre or emergency area
- Administer tetanus toxoid, antibiotics if indicated
- Stop bleeding by compression with sterile gauze; if necessary, extend wound, being careful not to cross skin creases in palm, digits
- Close wounds only when clean, using suture, spontaneous healing or skin grafts
- Debride, lavage all wounds in operating theatre or emergency area
- If contaminated, delay closure until after second debridement
- Wounds <1 cm will granulate spontaneously
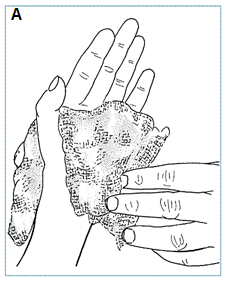 |
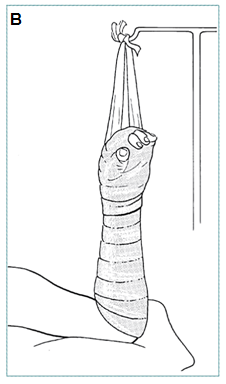
- Cover with sterile gauze (A)
- Apply plaster splint to hold wrist in 20o extension, fingertips exposed
- Elevate limb for first week to reduce oedema (B)
- Begin active exercises as soon as possible
- Inspect wound in 2-3 days to remove drains
|
 |
SPECIFIC LACERATIONS: Tendons